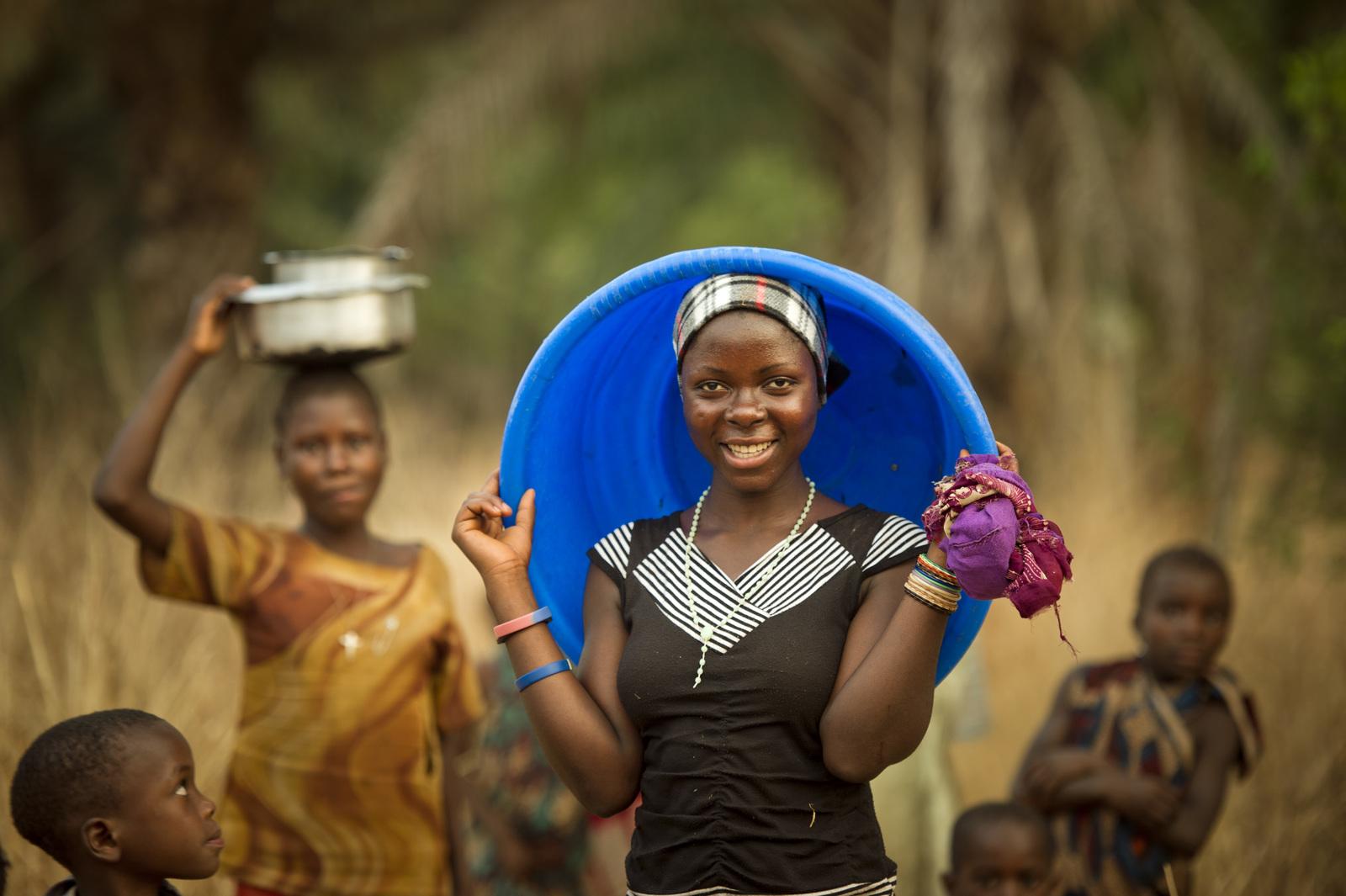
Defining Population Dynamics, Health and the Environment
Ongoing population growth poses specific challenges in the African Great Lakes. As the population increases, more and more natural resources are needed to support them. Over 60 percent of residents of the African Great Lakes region depend on farming for their livelihood. The rapidly increasing human population puts pressure on agricultural land. When agriculture can’t employ or feed everyone, people turn toward the fish industry. But, the fisheries in most lakes are already declining and likely can’t survive additional pressure. At the same time, almost 40 percent of the population—over 100 million people—lack clean water and almost 75 percent lack improved sanitation. As the population grows, these numbers are expected to rise.
Population, Health and the Environment (PHE) is a community-based integrated development approach that seeks to mitigate these pressures and their severe public health impacts. This approach includes interventions like increasing access to health services (e.g., reproductive health) while helping communities manage their natural resources, thereby contributing to the conservation of critical ecosystems, improving human health, promoting adaptation to climate change, building resilience and promoting conservation and development.
Why It Matters
Why It Matters - PHE
Gathering Water
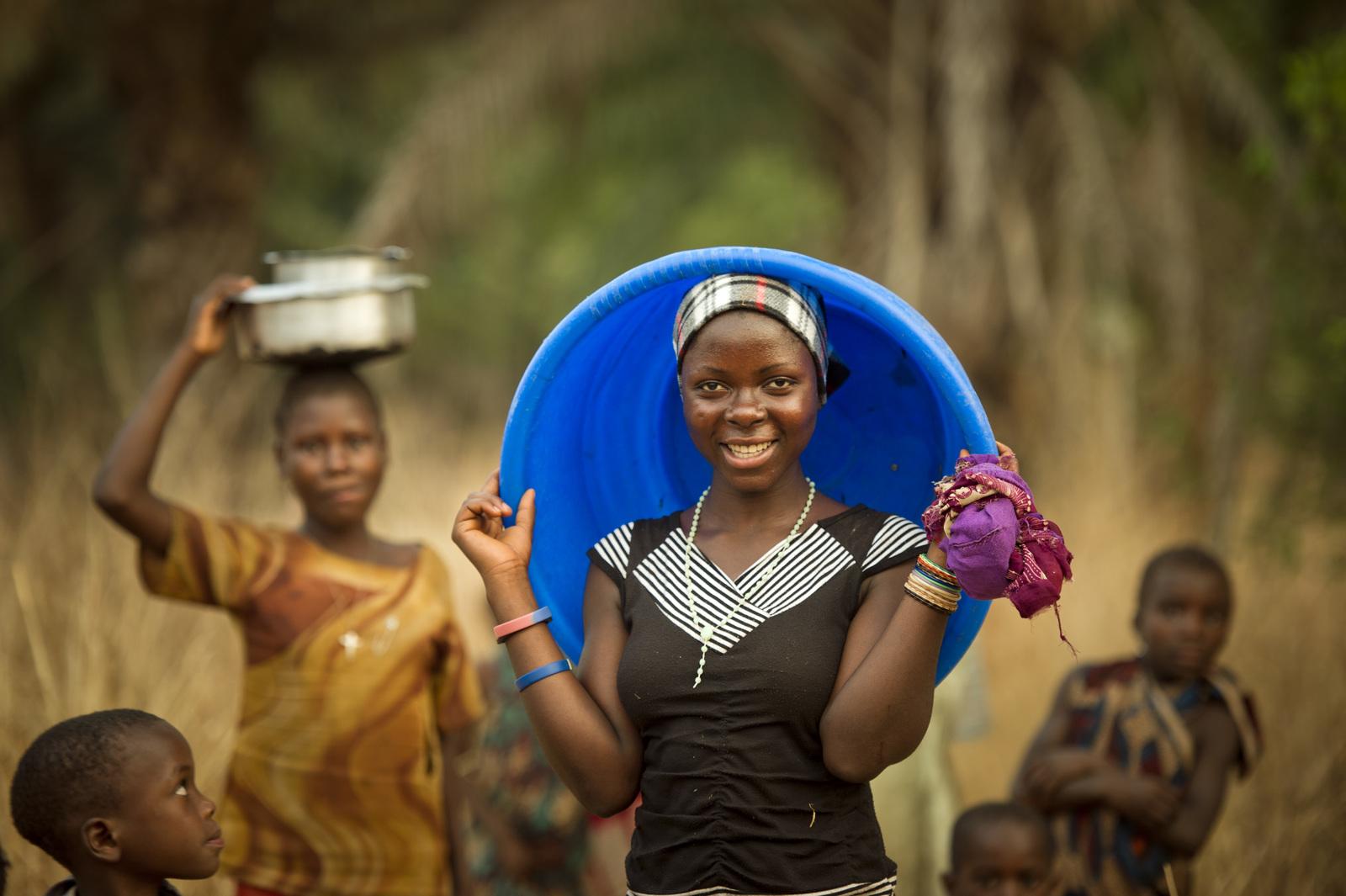
Almost 40 percent of the population in the AGL region lack access to clean water. Population growth is likely to exacerbate this problem.
Source: Swema Kabliya walks to get water in the village of Nkonkwa, on Lake Tanganyika in Tanzania. Ami Vitale
HoPE-LVB: Health Services
As population grows and natural resources are exploited, public health deteriorates. Reproductive health programs can address these issues.
Source: HoPE-LVB
Family
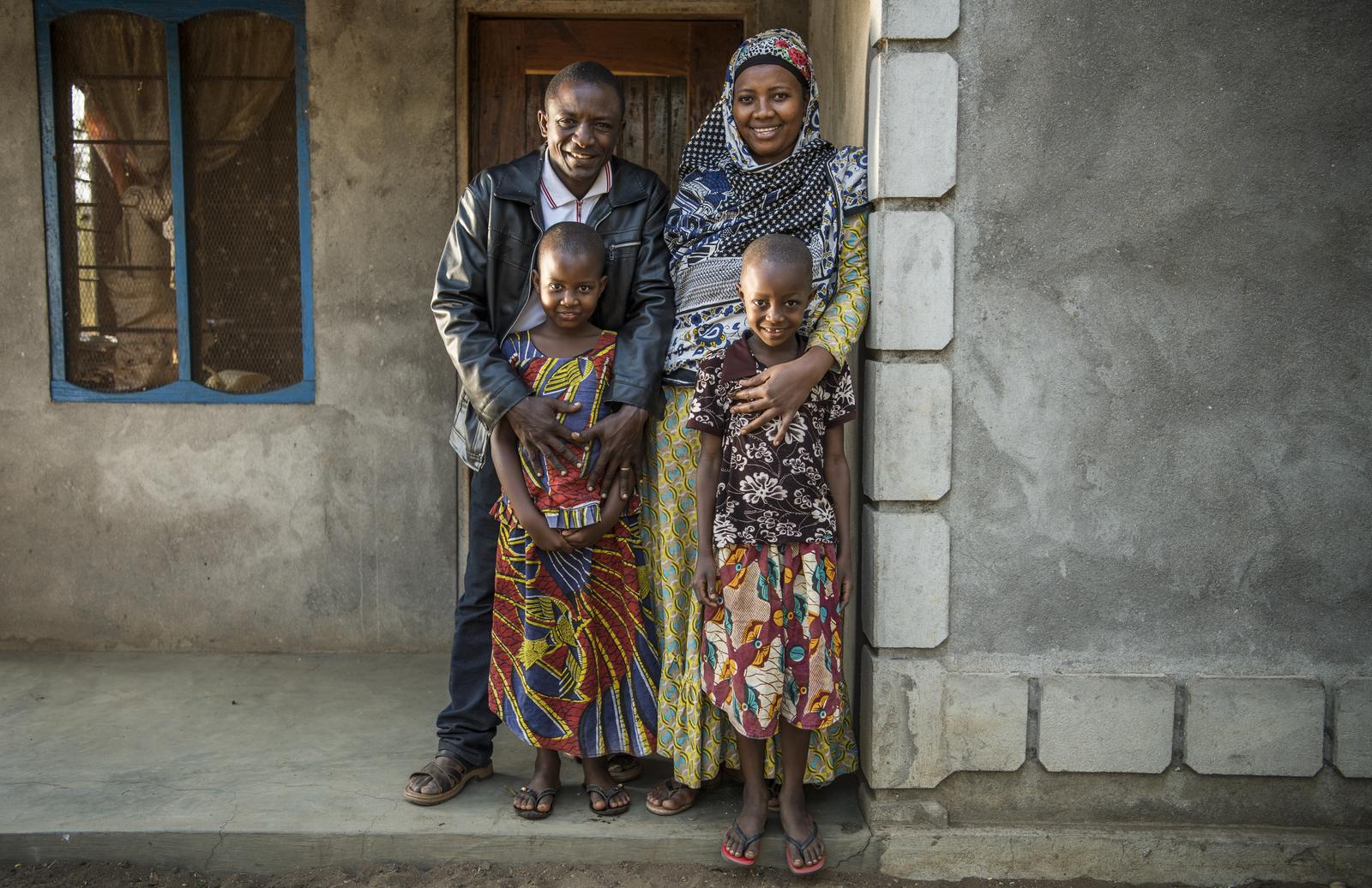

Working at the community level to create model households can improve public health and environmental behaviors.
Source: Ashura Katunka, her husband Mohammed Maulid Katunka, and children Hajira (left) and Hailatai stand in front of their home in the village of Mgambo on Lake Tanganyika. Ami Vitale
Focus Areas
African Great Lakes Inform provides resources to managers, researchers and stakeholders across the AGL region who are focused on the interaction between population, health and the environment. Entities working on this theme are focused on the following:
- Exploring how population dynamics, health and the environment interact with conservation and development
- Creating targeted interventions to address these issues through approaches such as women’s empowerment and resilience, the “Demographic Dividend” and family planning
- Integrating PHE with global sustainable development goals
- Avoiding unintentional natural resource consequences in large scale human health interventions
- Studying the impacts of environmental degradation on local community health
- Investigating resource restoration potential
- Linking population dynamics with resilience to climate change